Achieving a successful business is basically impossible without marketing demand. No matter how revolutionary your ideas and products seem to be, without customers wanting to invest their hard-earned money and make purchases, you won’t get revenue. That’s why finding product-market fit is crucial before you start working on your Minimum Viable Product (MVP) creation.
In this article, we’ll look into the matter of product-market fit and study the best methods and major steps to achieving it successfully.
What is Product-Market Fit?
Let’s start our guide with a comprehensive product-market fit definition.
The term “product-market fit” was first used in 2007 by American investor and entrepreneur Marc Andreessen, who describes it as “identifying a good market with a product capable of satisfying that market.”
Frequently, we witness businesses developing products without first comprehending the issues, requirements, and potential solutions of their users. However, even superior product delivery is useless if you aren’t providing the appropriate solution for the relevant issue or some other kind of value.
When you create a product that meets the needs of your customers, you are achieving product-market fit. Top brands and market leaders are frequently set apart from the competition by finding the ideal product-market fit.
Although it’s a straightforward idea, it can be challenging to implement in real life. A significant portion of the challenge is being able to fully comprehend your present and potential clients in order to appropriately meet their demands. To get there, a product team must put in a significant amount of work and conduct a great deal of research.
Why is Product-Market Fit Important?
Your business cannot expand unless you have a product that enough people will purchase to generate a steady profit. Achieving product-market fit has several advantages.
- Attracting Investors
As we mentioned, whether a startup achieves product-market fit can be a major identifying factor for investors. They frequently seek proof of product-market fit. This is because a company’s business model is essentially validated by product-market fit, and discovering it opens up growth prospects.
- Business Growth
To ensure the expansion of your business in an organic way, you need to establish that the market is ready to receive your offer. Without confirming it and achieving a perfect balance in your business-market relationships, you cannot effectively build strategies for growth. Moreover, businesses without PMF don’t see an increase in revenue while spending money on product creation and marketing, so their limitation of resources impedes growth. Product-market fit leads to organic, non-paid growth for businesses.
- Productivity
Your team cannot afford to concentrate on other crucial strategic goals like growth or upselling current users until you have developed a product that you are certain enough people are prepared to pay for. If you haven’t initially established that your product has a sufficient market to support itself and turn a profit, those efforts may even be counterproductive.
- Stable Profit
Getting a stable revenue is one of the main short-term goals of every business. It’s important for your current financial state as well as prospects and scaling opportunities.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Keep customers by finding out who is satisfied with your product and why. Find the features that customers value most in your products to satisfy them and encourage them to purchase.
- Scalability
Your business will have fewer growing pains and be able to expand on its existing well-functioning system if you have a clear grasp of what you offer to customers.
- Market Recognition
The fact that people are discussing and recommending your product to friends, family, and coworkers is one of the most important measures of product-market fit. Your brand’s visibility in the marketplace gets improved by this word-of-mouth advertising, which also can help you in positioning as an industry leader.
Product-Market Fit Examples
Some businesses have done such a great job of developing a product that fits the market that you can use their achievements as models for your product launch, customer development initiatives, or product process. Examine the following examples to have a better understanding of product-market fit and the potential long-term effects.
Spotify
In 2008, Spotify made its debut in the music streaming market by providing customers with on-demand access to a sizable music collection in exchange for a monthly membership fee. Customers looking for easy and reasonably priced access to music were drawn to this creative strategy, which upended the established music business. Additionally, Spotify’s freemium business model, which offers a basic version with advertisements and a premium version without, enables consumers to test out the platform’s worth before deciding to pay for a membership.
Uber
Uber first offered free rides at local tech events in San Francisco to create product-market fit. Uber’s co-founders recognized the taxi system’s exorbitant expenses and antiquated design, which resulted in low usage. It started offering new users a 50% discount as the app grew in popularity.
Experts point to Uber’s ability to solve an issue and create demand at the same time. Although they weren’t actively looking for a better taxi service, customers welcomed the concept as soon as a more practical and approachable substitute was offered. As a result, consumers began sharing their experiences on social media, which gave the startup social proof and created the network effect.
Zoom
With the COVID-19 epidemic causing a sharp rise in remote work and virtual meetings, Zoom Video Communications had a huge spike in popularity in 2020. It became a popular choice for both individuals and companies because it offered a dependable and easy-to-use video conferencing platform. Zoom’s success and quick expansion show how effective product-market fit can be. The startup Zoom was able to develop a product that connected with users and achieve extraordinary success by recognizing and solving a need for people who wanted to communicate with others digitally, such as students or remote workers.
How to Find Product-Market Fit
Product-market fit is also one of the key concepts used by the Lean startup methodology, which offers a structural approach to its understanding. You can see this structure and the characteristics that define product-market fit in the Product-Market Fit Pyramid.
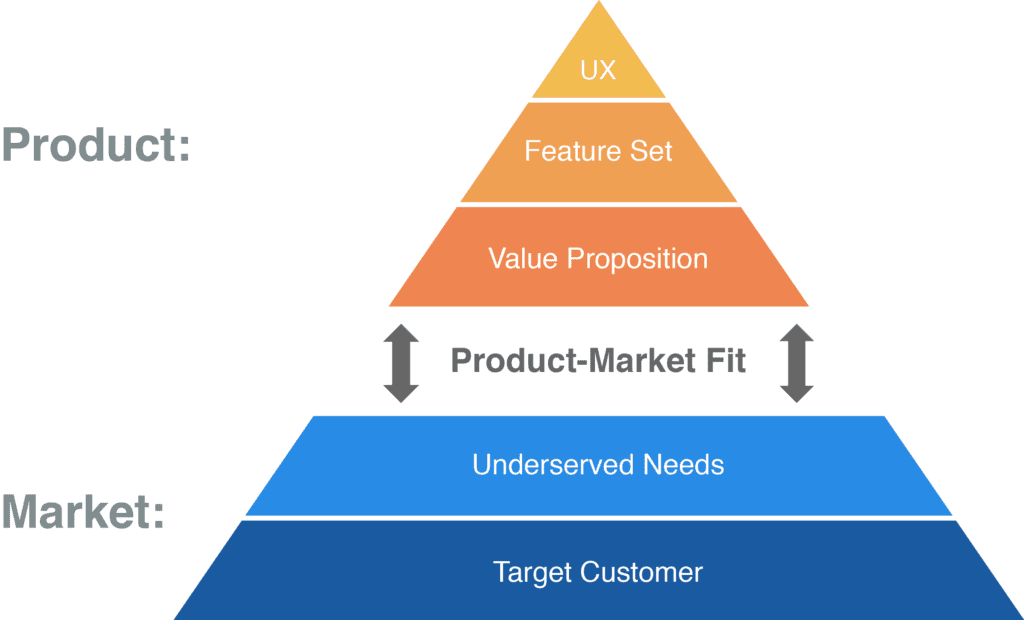
This PMF (product-market fit) Pyramid outlines the connection between different layers of the market and product.
Ultimately, the PMF pyramid clarifies that we must identify the target customer and unfulfilled customer demands before developing the product. It is wasteful to build a product without that defined.
Similar to this, we must first identify the value proposition of the product (based on the demands of our market) before we can define the user experience.
With this understanding, you can now follow through with the process of finding product-market fit. Here, we’ll share the two most popular methodologies.
Lean Product Six-Step Method
The first method of how to find product-market fit that we want to introduce is a 6-step program outlined in The Lean Product Playbook.
There are six steps in the Lean Product Process:
- Identify your target customer.
- Determine the unmet needs of your customers.
- Describe your value proposition.
- Give an example of your MVP feature set.
- Make your MVP prototype.
- Test your MVP with customers.
Let’s examine each of these steps in detail to give you a comprehensive plan on how to achieve product-market fit.
Step 1: Identify Your Target Audience
Market segmentation is a useful tool for identifying your target client. To ensure that everyone on the product team knows for whom they should be planning and developing the product, personas are an excellent tool for describing your target consumer.
Step 2. Recognize the Needs of Your Customers
It’s not enough to define your ideal customer. Making a product for an already-existing solution on the market is not feasible. Determine the problems that your potential client faces and create a solution to close the market gap.
Customer interviews, product research, on-site surveys, and behavior analytics are all things you can start doing.
Step 3. Determine Your Value Proposition
Customers have a compelling incentive to purchase from you because of your value proposition, also known as your unique selling proposition, which sets you apart from the competitors.
- When creating your value proposition, consider the following questions:
- What are the main issues that your consumers are facing?
- What are the qualities and advantages of your product?
- What distinguishes your product from others on the market that provide the same solution?
- Which of your features or offerings successfully alleviates the problems faced by your customers?
These inquiries will assist you in determining why your product is most appropriate for resolving the issues of your clients.
Offering something that customers aren’t already receiving from other items is a smart way to define your value proposition.
Step 4: Define Your MVP Feature Set
After your value proposition is apparent, you must define the features that your minimal viable product must have. Building only what is necessary to generate enough value in your target customer’s perspective to confirm that you are on the right track is the goal of the MVP approach.
Customers may inform you that a crucial feature is missing from your MVP. Or they can say that a feature you choose to include in your MVP is not something they would utilize. Iterating until you have an MVP that customers believe is feasible is the aim.
Step 5. Make Your MVP Prototype
Make a basic product instead of worrying about developing your entire concept. Once you have input from customers, you can make changes to it.
Step 6. Test MVP on Your Customers and Iterate
Present your product to some prospective buyers. Ask customers for their opinions. Allow them to become aware of it and experience it for themselves. Find out what they like and dislike about it. Instead, what would they like to see? Remain receptive and adaptable to criticism so you may modify your concept to precisely suit the requirements and desires of your clients.
Three Rings Method
The Three-Rings Framework breaks the journey to product-market fit into a series of smaller milestones, visualized as a set of rings that you close in sequence as you make your way up the hockey stick curve.
- 1st — the Founder Ring (You)
What do you have a special passion for? What abilities, perceptions, or unfair advantages do you contribute?
- 2nd — the Customer Ring (Who)
For whom are you providing a solution? What are their motivations, behaviors, and areas of pain?
- 3rd — the Market Ring (Why Now)
Is the market underserved or expanding? Are there any tailwinds (trends, changes in technology) that make now the ideal moment?
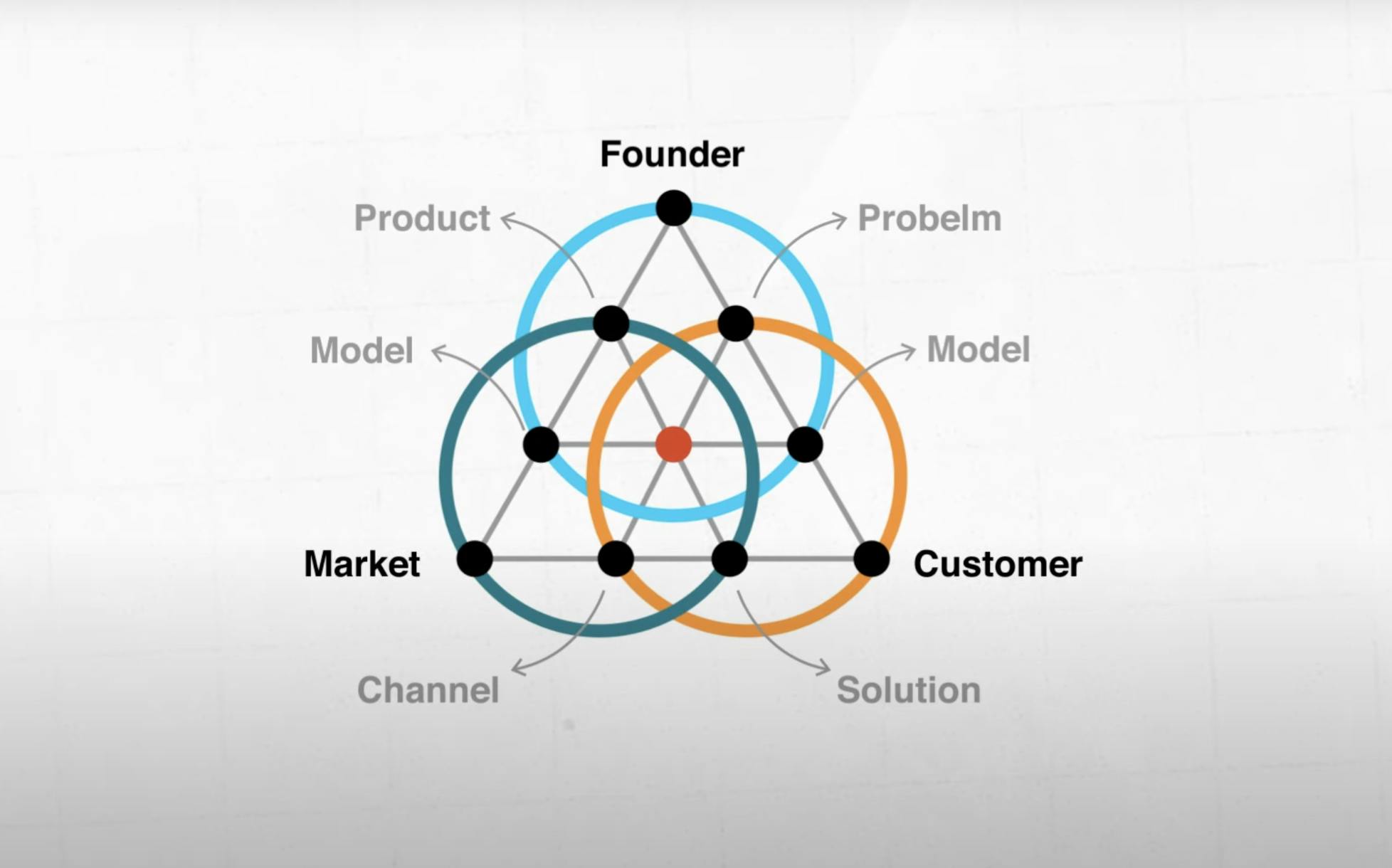
The framework is based on the idea that an entrepreneur’s real product is a viable business model rather than just a workable solution.
Because it enables us to apply the concepts of product development to business models, considering a business model as a product is especially empowering. Business models can be constructed in phases, just like a product.
The framework’s three rings correspond to the three steps involved in creating a viable business plan:
- Business Model Design Stage
- Validation Stage
- Growth Stage
Stage 1: The Founder Ring
This is where you, as the founder, create a plan for your business concept.
Any complicated project would require some sort of architectural sketch or blueprint before building could begin. However, it is a costly error for many founders to omit this phase while starting a business.
A solid blueprint helps you think more clearly and steer clear of common errors, but it does not ensure success. You can allocate your limited resources to the most promising ideas rather than squandering time on less-than-ideal ones.
The Founder Ring consists of three key segments:
- Founder-Goal Fit
An excessive number of founders begin by evaluating the potential size of a concept. However, wouldn’t you always begin with your most promising concept if you had three? You ought to begin with a goal rather than an idea. Estimating your maximal upside potential is not something I advise, though, as it is too distant from product-market fit. Rather, establish your minimum success criteria, which is the smallest result you must attain in three years or fewer for your project to be considered successful.
- Goals-Model Fit
After establishing your objective, use a template to transform your idea into a business model. This aids in breaking down your concept into fundamental presumptions that must fit together like a puzzle. Then, just as architects test their plans before construction, validate these assumptions against your minimum success criteria. Before spending extra time, money, and energy, make revisions to your business model if it doesn’t satisfy your requirements.
- Model-Founder Fit
Finally, ensure that your business model aligns with your personal mission, vision, and strengths. Startups are roller coasters that test your perseverance. Not all business models that work on paper will work for all founders.
Stage 2: The Customer Ring
Building the basis for your business model is the next stage after creating the plan. Every business model is predicated on assumptions, and your idea will fail if those assumptions are incorrect.
For the majority of items today, customer and market risks are more dangerous than technological viability—we can create nearly anything. The question is, will anyone be interested?
There are three main parts to the Customer Ring:
- Customer-Problem Fit
Consumers are more concerned with their issues than with your answer. Your solution won’t draw attention if it doesn’t address a significant enough issue. Carefully planned customer interviews are the best method to verify this. A problem that is thoroughly understood is half-solved.
- Problem-Solution Fit
Knowing your customers’ issues well will help you come up with a solution they will be interested in. Show customers a demo before spending months creating something they won’t want. You’re on the correct track if the demo convinces them to buy.
- Solution-Customer Fit
Convert your demo into an MVP and end the Solution-Customer Fit section if you can convince enough clients to buy it. Your business model’s ability to generate, deliver, and capture value has now been confirmed.
Stage 3: The Market Ring
The Market Ring, the last ring to close, is where you reach product-market fit and grow and scale to the hockey stick curve’s inflection point.
- Market-Channel Fit
To reach customers, begin testing scalable channels. Your audience and budget will determine which channels are best for you. Use quick, brief trials to evaluate multiple channels in parallel because it’s not always clear which will perform best.
- Channel-Product Fit
When you find a channel that shows promise, focus even more on it. Your product may need to be optimized for that channel.
How to Measure Product-Market Fit
Some definite measurements and criteria can help you assess whether you achieved a successful product-market fit. The evaluation process is important since it allows you to identify what stage your business is on right now and how to optimize your strategy in the future. Analysts and strategists use two major types of measurements, which are quantitative and qualitative metrics. Here are the main rates and characteristics that define your progress status.
Quantitative Metrics for Product-Market Fit Assessment
The rate at which consumers discontinue doing business with you. A high turnover rate indicates that customers are dissatisfied with your product, whether it be the features or the customer care, since they are leaving it by canceling renewals or unsubscribing. You may not be attaining product-market fit if your churn rate is high.
- Growth Rate
The rate at which certain variables, such as sales and client base, increase over a given time frame. A high growth rate indicates that sales of your products are increasing rapidly, which may indicate that you’ve discovered a perfect fit.
The proportion of customers who stick with your tool or app after registering is known as the user retention rate. A high user retention rate may indicate that you have found a fit because it indicates that customers are satisfied and want to keep using your product.
- Market Share
This is the proportion of the market’s total sales that your business generates. A large market share indicates that consumers favor your product over competing ones, positioning you as a major force in the sector. A significant sign that you have achieved product-market fit is a dominant market share.
- NPS
A measure of a customer’s devotion to your product based on how often they advocate and promote it is called the Net Promoter Score (NPS). A high NPS indicates that your product is well-liked by consumers and that they are spreading the word about it through recommendations.
Qualitative Metrics to Evaluate Product-Market Fit
- Word-of-Mouth and Referrals
As Andreessen states, your consumers essentially act as your product’s sales representatives if they tell others about it. The more people who find you through word-of-mouth and referrals, particularly loyalty programs, the more your product expands. You may learn how your customers came up with your product and whether they would suggest you to friends and coworkers by using surveys and other feedback-gathering techniques.
- Publicity and Media Coverage
If you receive a lot of calls from media outlets and are frequently featured on social media and online news channels, your visibility grows and helps the business and product expand.
What Happens After Product-Market Fit
After achieving product-market fit, you still have a lot of work to do since this is just the starting point of the real growth of your business. Missing this pivotal moment can lead to your brand lagging behind the competitors. While there are a lot of tasks to be prepared for, here we gathered some major startup development aspects that should be in your focus.
Focus on Customer Retention
In addition to growing your clientele, you also want to keep your current audience by promoting upgrades or repeat business.
If your clients are still pleased with your product, they will probably tell others about it. Since trust is already established in the relationship between the two parties, word-of-mouth advertising is among the most successful types of advertising.
Building strong relationships with your customers benefits your business in several ways, one of which is making it simple to obtain insightful feedback on how to enhance your product going forward.
Working on Growth Rate
Upon achieving product-market fit, it’s time to increase sales. Making sure that your business continues to turn a profit and increases sales, dividends, and income is crucial. Long-term maintenance of the product-market fit position will provide you with a base on which to grow. Periodically check income and profitability to stay on course.
Growing Your Market Share
Market share is another aspect to monitor as you increase your production, marketing, and sales. Since you probably can’t obtain information from your competitors, market share is a challenging indicator to measure. However, market research on your competitors and your own quarterly reports might be used to estimate it. This can assist you in evaluating your overall success throughout the previous time frame with the market as a whole.
Customer Feedback and Engagement
Customer engagement and opinions play a major role in attaining product-market fit. Prior to product-market fit, you had to concentrate on qualitative input in order to enhance the product. You should shift your attention to engagement when you’ve achieved product-market fit. Your success evaluation during this process should be based on statistics. As you scale up, your statistics will tell you if you are still engaging your target audience.
Moving to the General Market
It’s critical to remember that early adopters are your initial clients who introduce you to product-market fit. These are the people who always try new products first. However, the majority of buyers require additional incentives to test your goods. Therefore, content that encourages potential buyers to put in the effort to try your product should be a part of your marketing strategies.
Signs You Haven’t Reached Product-Market Fit
The following are typical signs that a startup has not yet attained product-market fit:
- Low User Engagement
It indicates that users do not believe the product to be very valuable if engagement measures, such as time spent on the app, repeat usage, or feature uptake, are low.
When customers leave a business quickly after registering or making a purchase, it’s usually because the product doesn’t live up to their expectations or adequately address their issue.
- Dependency on Steep Discounts
Having to constantly provide discounts to draw clients may indicate that the product’s perceived worth is below its asking price.
- Misalignment with Customer Needs
It is shown by customer feedback, which may show that the product is not effectively addressing the main problems.
- Low Paid Subscription Purchases
Low rates of customers switching from free trials to the paid product can be a sign that the product is not connecting with its target audience sufficiently.
- Misconceptions by Users
If users frequently misinterpret the product’s main features or goal, it may be a sign that the messaging behind the product is not aligned with the demands of the market.
- Inconsistent Growth Patterns
A lack of product-market fit may be indicated by erratic growth or user acquisition that is only feasible with unsustainable marketing expenditures.
- Low NPS
A low or steadily dropping NPS may indicate that consumers are not eager to recommend the product to others.
- Limited Organic Advocacy
If there aren’t enough natural, uninvited user recommendations or endorsements, it may be a sign that the product isn’t having a significant enough effect to encourage consumers to spread the word.
- Preference for Competitors
It’s a clear sign that your product lacks a significant competitive edge if customers like competitors’ solutions, even if they are more costly or feature-rich.
- Regular Need for Modifications
A firm that regularly modifies its target market, strategy, or product characteristics to expand is probably not finding a market for its first offering.
- Customer Support Overload
A high number of support tickets, particularly on basic features or benefits of the product, may be a sign that customer expectations and product performance are not aligned
Signs You Might Have a Strong Product-Market Fit
- Organic Growth Surpasses Paid Efforts
When startups get clients mostly through organic search, word-of-mouth, or in-person visits, it means their product is connecting with the market sufficiently to generate interest and advocacy on its own.
- Retention Curves Flatten
Rather than declining sharply after initial use, the number of active users stays constant over time. This suggests that the product is long-lasting.
- Growth in Customer LTV
A rising lifetime value (LTV) indicates that customers find the product valuable over time, which may result in repeat business, upselling opportunities, or subscription renewals.
- Decreased Sensitivity to Price Changes
Customers may believe the product is worth more than its price if price increases do not result in a notable drop in new user acquisition or churn.
- High NPS
Strong customer satisfaction and a propensity to refer the product to others are indicated by a high or rising NPS.
It’s an indication of engagement and a good fit when people produce content about your product, such as blog entries, videos, or forum conversations.
- Capacity to Support Growth
A business is operationally ready and market-fit if it can accommodate growth without compromising the quality of its product or customer experience.
- Account Expansion
In the business-to-business (B2B) industry, it is a definite indication of perceived value and fit when current clients spread the product’s use throughout their company.
- Sales Cycle Compression
As the market starts to comprehend and accept the product more easily, the period from the first lead to the closed sale gets shorter.
- Positive Analyst Recognition
When industry analysts give a product a positive evaluation or award, it shows that they believe it will be relevant and long-lasting in the market.
- Interest in Strategic Investments
When strategic investors, like those in your market or industry, express interest, it indicates that they believe the product will be a successful addition to the market.
- No Recruiting Issues
The reputation of the brand and the products draw in top individuals ready to join a thriving business.
- Involvement of Suppliers and Partners
Vendors and possible partners are eager to work together, a sign that they recognize the product’s market potential and wish to be linked to it.
- Competitive Reaction
As a result of the product’s market influence, rivals start to alter their pricing, features, or strategies.
FAQ
Who is responsible for product-market fit?
Any team that works with the product or service and the customer is accountable for product-market fit. The value proposition for the customer is created and fulfilled by a variety of processes, including product development, marketing, production, testing, and sales.
What is product-market matching?
Finding the ideal combination of product and value proposition to appeal to your target market is known as product/market matching. Knowing which potential products may be marketed to a target audience that is most likely to purchase them should be your first step.
Is using a product once an indicator of product-market fit?
No, a single use of a product does not indicate product-market fit; rather, it necessitates high retention, frequent usage, and evident target market desire.
How long does it take to achieve product-market fit?
For the majority of products, achieving product-market fit takes about two years on average, and 80% of them never do. This can be transformed into a more methodical and structured procedure with the correct mindsets and thought processes. To achieve long-term profitability, everything hinges on how fast you can finish your market research and offer value to your target audience.
Conclusion
Product-market fit is a method that combines a company’s sales objectives with the input and involvement of the target market to help the business enhance the product. It needs a team of committed individuals that collaborate throughout the process. When it comes to the marketing part of the strategy for achieving product-market fit, you can trust Flowium to be there for you on this journey. As a seasoned email marketing agency with 8+ years on the market, we have helped various businesses to accomplish their promotional and growth goals. Contact us now to receive expert assistance!







